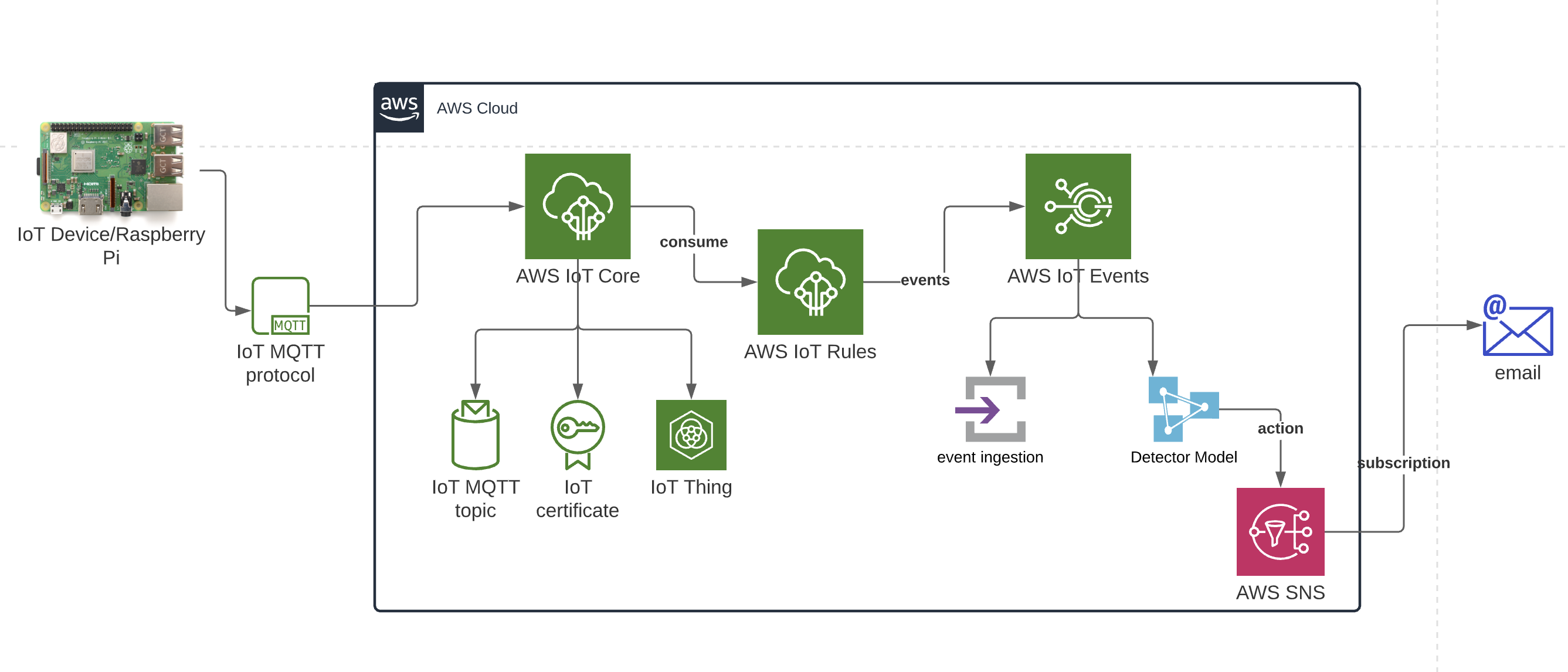
Imagine having a little computer, a Raspberry Pi, out in the world, doing its thing, but you need to check on it, update it, or maybe even give it new instructions. This idea of reaching out to devices far away, keeping them safe and working, is what remote IoT is all about. It's pretty important, too, especially as more and more smart gadgets become part of our daily lives, from home automation setups to industrial sensors. Getting that connection right, making sure it's stable and secure, can sometimes feel like a puzzle, but it's a puzzle worth solving for peace of mind.
That's where a Virtual Private Cloud, or VPC, and something called SSH come into play. These tools work together to build a strong, private tunnel right to your Raspberry Pi, no matter where it is. Think of a VPC as your own personal, walled-off section of the internet, where only your approved devices can hang out. And SSH? Well, that's the super-secure way you talk to your Pi once you're inside that private space. It's a bit like having a secret handshake and a special key to get into a very exclusive club.
This article is going to walk you through the journey of setting up your Raspberry Pi for secure remote access, particularly within a VPC, using SSH. We'll touch on the crucial steps, including where to find the necessary "downloads" to get your Pi ready for its big adventure. It's about getting your `remoteiot vpc ssh raspberry pi download` process sorted, so you can manage your little computers with confidence.
Table of Contents
- What is Remote IoT and Why a Raspberry Pi?
- Understanding VPCs for Secure IoT Deployments
- SSH: Your Secure Gateway to the Pi
- Getting Started: The "Download" Aspect
- Connecting Your Pi to the VPC
- Troubleshooting and Advanced Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Remote IoT and Why a Raspberry Pi?
Remote IoT is basically about connecting to and managing "things" that are not right next to you. These "things" could be anything from a smart thermostat in your home to a sensor array in a distant field. The idea is to gather data, send commands, or perform updates without needing to be physically present. It's a very useful concept, especially for projects that span large areas or require constant oversight.
The Appeal of Raspberry Pi
The Raspberry Pi, a tiny, affordable computer, has really captured the imagination of makers and innovators everywhere. It's quite versatile, capable of doing so much, from running a small web server to controlling robots. Its small size, low power consumption, and open-source nature make it a perfect candidate for IoT projects. You can, for instance, put one almost anywhere and it can start collecting data or performing tasks.
A Pi is also pretty good for learning about computing, too. It offers a lot of ways to experiment with hardware and software, making it a favorite for both beginners and seasoned developers. Its community is huge, which means there's a lot of help available if you ever get stuck, which is a nice thing to have when you're trying something new.
Why Remote Access Matters
Imagine you have a Raspberry Pi monitoring the temperature in your greenhouse, which is miles away. You can't just drive there every time you need to check a reading or adjust a setting. This is where remote access becomes absolutely essential. It allows you to interact with your Pi as if you were sitting right in front of it, but from the comfort of your home or office.
Being able to access your Pi remotely also helps with maintenance and updates. Software needs patching, and sometimes things just go wrong. With remote access, you can fix issues, deploy new code, or simply restart the device without a physical trip. This is, in a way, a huge time-saver and makes managing a fleet of devices much more practical.
Understanding VPCs for Secure IoT Deployments
A Virtual Private Cloud, or VPC, is a private network that lives within a larger public cloud environment. Think of it as your own isolated section of a big apartment building. You get to decide who has keys to your apartment and what kind of security measures are in place. This separation is very important for keeping your devices safe from the wider internet's various threats.
What a VPC Brings to Your Pi
When you connect your Raspberry Pi to a VPC, you're essentially giving it a secure, private space to operate. This means your Pi isn't directly exposed to the public internet, which can be a bit like leaving your front door wide open. Instead, it communicates through controlled pathways you set up. This dramatically reduces the chances of unauthorized access or malicious attacks.
A VPC also allows you to configure very specific network rules, like firewalls and routing tables. You can, for instance, dictate exactly which types of traffic are allowed in and out, and from where. This level of control is pretty much essential for any serious IoT deployment, giving you peace of mind that your data and devices are well-protected. It's a lot like having a dedicated security team for your network.
Setting Up Your VPC Environment
Setting up a VPC involves a few steps, and it can vary slightly depending on which cloud provider you use, like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. Generally, you'll define your network's IP address range, create subnets (smaller sections within your VPC), and set up routing tables to direct traffic. You will also typically configure security groups and network access control lists (NACLs) to act as firewalls, controlling what traffic can flow.
For your Raspberry Pi, you'll usually place it in a private subnet, meaning it won't have a direct public IP address. To reach it, you might use a "jump box" or a VPN connection that is itself within the VPC, which acts as a secure intermediary. This approach adds another layer of security, making it quite difficult for anyone outside your VPC to even see your Pi, let alone connect to it.
SSH: Your Secure Gateway to the Pi
SSH, which stands for Secure Shell, is a network protocol that allows you to connect to a remote computer securely. It provides a strong, encrypted connection between your local machine and your Raspberry Pi. This means that any data you send back and forth, like commands or files, is scrambled and protected from prying eyes. It's a very common tool, used by pretty much anyone who manages remote servers.
The Role of SSH in Remote Access
When you use SSH to connect to your Raspberry Pi, you're essentially opening a secure command-line interface. This gives you full control over the Pi, allowing you to run commands, edit files, install software, and troubleshoot issues. It's the primary way many developers and hobbyists interact with their headless (no monitor, keyboard, mouse) Pis.
The security of SSH comes from its use of encryption. When you initiate an SSH connection, a secure channel is established, and all communication through that channel is encrypted. This is very important for IoT devices, as they often handle sensitive data or control physical systems. Without strong encryption, your commands could be intercepted, or your data stolen, which is something nobody wants.
SSH Key Management and Best Practices
While SSH can use passwords, the most secure way to connect is with SSH keys. An SSH key pair consists of a public key and a private key. You keep the private key secret on your local machine, and you place the public key on your Raspberry Pi. When you try to connect, the Pi challenges your machine, and if your private key matches the public key, access is granted. This method is far more secure than passwords, which can be guessed or cracked.
It's a good idea to protect your private key with a strong passphrase, too. Treat your private key like you would a very important house key; you wouldn't just leave it lying around. Regularly reviewing and rotating your SSH keys is also a wise practice, especially if you have many devices or team members accessing them. This helps keep your remote IoT setup very secure, preventing issues like unauthorized access, similar to how one might carefully check for "unauthorized automatic payments" on financial accounts.
Getting Started: The "Download" Aspect
Before you can connect to your Raspberry Pi, you need to get its operating system onto an SD card. This is where the "download" part of our discussion really comes into play. You'll need to download the appropriate Raspberry Pi OS image, and then "burn" it onto an SD card so your Pi can boot from it. This is a fundamental first step for any new Pi project.
Choosing Your Raspberry Pi OS
The most common operating system for Raspberry Pi is Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian), which is based on Debian Linux. There are a few versions available. For most remote IoT projects, you'll likely want the "Lite" version, which doesn't include a desktop environment. This makes it smaller, faster, and uses less memory, which is perfect for a device that you'll be accessing purely through the command line via SSH.
You might also consider other operating systems depending on your project's needs, like Ubuntu Server or specialized IoT distributions. Each has its own benefits, but Raspberry Pi OS Lite is usually the best starting point for general purpose remote IoT. It's a good idea to pick one that has a lot of community support, too, as that makes troubleshooting easier.
Where to Download and Verify
The official place to download Raspberry Pi OS images is the Raspberry Pi Foundation's website. It's important to always download from official sources to ensure you're getting a legitimate and uncorrupted image. Just like when you might use a "Chrome inspector" to find the right audio or video link, or verify details, you should always check the source for your Pi's operating system.
After downloading, it's highly recommended to verify the integrity of the downloaded file using a checksum (like SHA256). This step confirms that the file hasn't been tampered with during download and is exactly what the official source intended. It's a bit like making sure the "key hash" matches what's expected, preventing issues that might arise from a corrupted or incorrect file, which could lead to connection problems later on. You want to be very sure that what you downloaded is exactly what you need.
Preparing Your SD Card
Once you have your Raspberry Pi OS image downloaded and verified, you'll need a tool to write it to your SD card. The Raspberry Pi Imager is the official and easiest tool for this purpose. It's available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, and it streamlines the process of selecting the OS and the SD card.
When using the Imager, you can also pre-configure some settings, like enabling SSH and setting up Wi-Fi credentials. This is a super handy feature for headless setups, as it means you won't need to connect a monitor or keyboard to your Pi for the initial setup. Just write the image, insert the card, and your Pi should be ready to connect to your network and accept SSH connections.
Connecting Your Pi to the VPC
Getting your Raspberry Pi to talk to your VPC is a very important step. It involves making sure your Pi is on the right network and that your VPC is set up to allow it to communicate securely. This part of the process brings together the physical device with your virtual private network.
Initial Setup and Network Configuration
After you've prepared your SD card and inserted it into your Raspberry Pi, you'll power it on. If you pre-configured Wi-Fi, it should connect to your network automatically. If not, you'll need to connect it to your local network via Ethernet or set up Wi-Fi manually (which might require a temporary monitor/keyboard setup if SSH wasn't enabled via Imager).
Once your Pi is on your local network, you'll need to find its IP address. Tools like `nmap` or simply checking your router's connected devices list can help with this. This IP address is what you'll use for your initial SSH connection from a machine that can reach your Pi on the local network. This is just a temporary step before getting it fully into the VPC.
Establishing the SSH Connection
With SSH enabled on your Pi and its IP address known, you can open a terminal or command prompt on your computer and use the `ssh` command. For example, `ssh pi@your_pi_ip_address`. If you're using SSH keys, it will attempt to authenticate automatically. If not, it will ask for the password for the 'pi' user (the default username).
Once connected, you can then configure your Raspberry Pi to join your VPC. This usually involves installing any necessary VPN client software or configuring network settings to route its traffic through your VPC's gateway. This might include setting up a secure tunnel, which is a bit like creating a private road from your Pi directly into your cloud network. It's a pretty direct path.
Troubleshooting and Advanced Tips
Even with the best planning, sometimes things don't go exactly as expected. Troubleshooting is a normal part of any technical setup, and remote IoT is no different. Knowing some common issues and how to approach them can save you a lot of time and frustration.
Common Connection Issues
If you're having trouble connecting via SSH, there are a few usual suspects. First, double-check that your Raspberry Pi is actually powered on and connected to the network. Is the network cable plugged in, or is the Wi-Fi signal strong? Next, confirm the IP address of your Pi; sometimes it can change. Firewall settings, both on your local machine and within your VPC, can also block connections. Make sure SSH (port 22) is allowed.
Sometimes, the issue might be with your SSH keys. Did you copy the public key correctly to the Pi? Is your private key protected with the right permissions on your local machine? Just like how you might use "network" tools in a "Chrome inspector" to diagnose why a web page isn't loading, checking network connectivity and SSH log files on both ends can give you clues about what's going wrong.
Enhancing Security
Beyond using SSH keys, there are more steps you can take to make your remote IoT setup even more secure. Changing the default username ('pi') to something unique is a very good idea. You should also disable password authentication for SSH once you have key-based authentication working smoothly. This means only those with the correct SSH private key can ever log in.
Keeping your Raspberry Pi's operating system and all installed software up to date is another critical security measure. Regular updates patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Also, consider implementing a firewall on the Pi itself, allowing only necessary incoming connections. This layered approach to security really helps protect your devices.
Monitoring Your Remote Pi
Once your Raspberry Pi is securely connected and running within your VPC, setting up some form of monitoring is a smart move. This could involve simple scripts that check disk space or CPU usage, or more sophisticated cloud-based monitoring services that keep an eye on your Pi's health and performance. Knowing what's happening with your device remotely is very helpful for proactive maintenance.
Monitoring can also alert you to unusual activity, which might indicate a security issue. For instance, if your Pi suddenly starts using a lot of network bandwidth when it shouldn't be, that could be a sign that something is amiss. Staying informed about your device's status helps you react quickly to problems, keeping your remote IoT operations running smoothly and securely, which is, you know, pretty important.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people often have about this topic.
How do I remotely access my Raspberry Pi from anywhere?
To access your Raspberry Pi from anywhere, you typically set it up within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and use SSH (Secure Shell) for encrypted communication. The VPC provides a private, secure network for your Pi, while SSH allows you to send commands and manage it from your local computer, even if you're miles away. You might connect to a "jump box" or VPN endpoint within your VPC first, then SSH to your Pi.
What is a VPC and why use it for IoT?
A VPC is a virtual private network section within a public cloud environment, giving you isolated network space. You use it for IoT because it offers enhanced security and control. Your Raspberry Pi won't be directly exposed to the open internet, reducing the risk of attacks. You can define strict firewall rules and network pathways, ensuring only authorized traffic reaches your devices, which is a pretty big deal for security.
Is SSH secure enough for Raspberry Pi remote access?
Yes, SSH is considered very secure for remote access, especially when configured correctly. The most secure way to use SSH is with key-based authentication, where you use a private/public key pair instead of passwords. It's also good practice to disable password logins, change default usernames, and keep your Pi's software updated. These steps, taken together, make SSH a very reliable and strong method for secure remote control.
Getting your Raspberry Pi set up for remote access within a VPC using SSH is a very practical skill for anyone interested in IoT. It brings together the flexibility of the Pi with the security and scalability of cloud networking. By following these steps, from downloading the right operating system to establishing secure connections, you can build a robust system for managing your remote devices. It's about empowering you to control your little computers no matter where they are, giving you a lot of freedom to create and innovate. For more general information on IoT device management, you might find this resource helpful. Learn more about secure remote access on our site, and link to this page here.


Detail Author:
- Name : Murray Franecki
- Username : lbernhard
- Email : boyer.lucienne@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1994-08-03
- Address : 9877 Bailey Club Suite 189 South Kennithport, VA 32250
- Phone : +18562581901
- Company : Bradtke, Rohan and Dare
- Job : Animal Husbandry Worker
- Bio : Voluptatem non doloribus sint. Vel voluptates ut qui qui fugiat repellat aut harum. Veritatis fugiat quia cumque doloremque. Enim fugiat quasi occaecati eligendi omnis quis ea.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/pierce_turner
- username : pierce_turner
- bio : Et praesentium eos non tenetur placeat. Sit accusamus quasi ut nihil cum in et. Doloremque eius iusto laborum quia molestias culpa molestias.
- followers : 5339
- following : 835
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/turner2018
- username : turner2018
- bio : Dolores magnam eum corrupti ad.
- followers : 2474
- following : 2906
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@pierce_official
- username : pierce_official
- bio : Et voluptatem ut sunt occaecati voluptatem.
- followers : 1349
- following : 2797
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/turner1981
- username : turner1981
- bio : Aut cumque velit voluptatem est inventore quia dolorem possimus.
- followers : 6622
- following : 1355

