Imagine being able to manage your smart home devices, those little gadgets that make life easier, from anywhere in the world. It's a pretty neat idea, isn't it? Yet, connecting to these Internet of Things (IoT) devices often means dealing with security worries. How do you make sure no one else can peek into your smart lights or tamper with your home automation system? Well, this is where a tool called SSH, or Secure Shell, comes into the picture, providing a really solid way to keep things safe and sound.
SSH is, in a way, like building a private, armored tunnel between your computer and your IoT device. It makes sure that any information passing through stays hidden from prying eyes. This means you can send commands, grab files, or even set up clever connections without worrying about someone else listening in. It's an important piece of the puzzle for anyone who has connected devices and wants to keep them secure.
In this guide, we will walk through how SSH works, why it is so important for your IoT setup, and how you can get it up and running. We will talk about connecting from different kinds of computers, how to make things even smoother with password-free logins, and some more advanced ways to use SSH for your connected gadgets. So, you know, let's get into making your smart devices truly secure.
Table of Contents
- What is SSH, Anyway?
- Why SSH is a Must-Have for Your IoT Devices
- The Principles Behind SSH: How It Keeps Things Safe
- Getting SSH Ready on Your IoT Device
- Connecting to Your IoT Gadget From Different Systems
- Making SSH Even Smarter for IoT
- Common Questions About SSH and IoT
- Keeping Your IoT Connections Safe for the Future
What is SSH, Anyway?
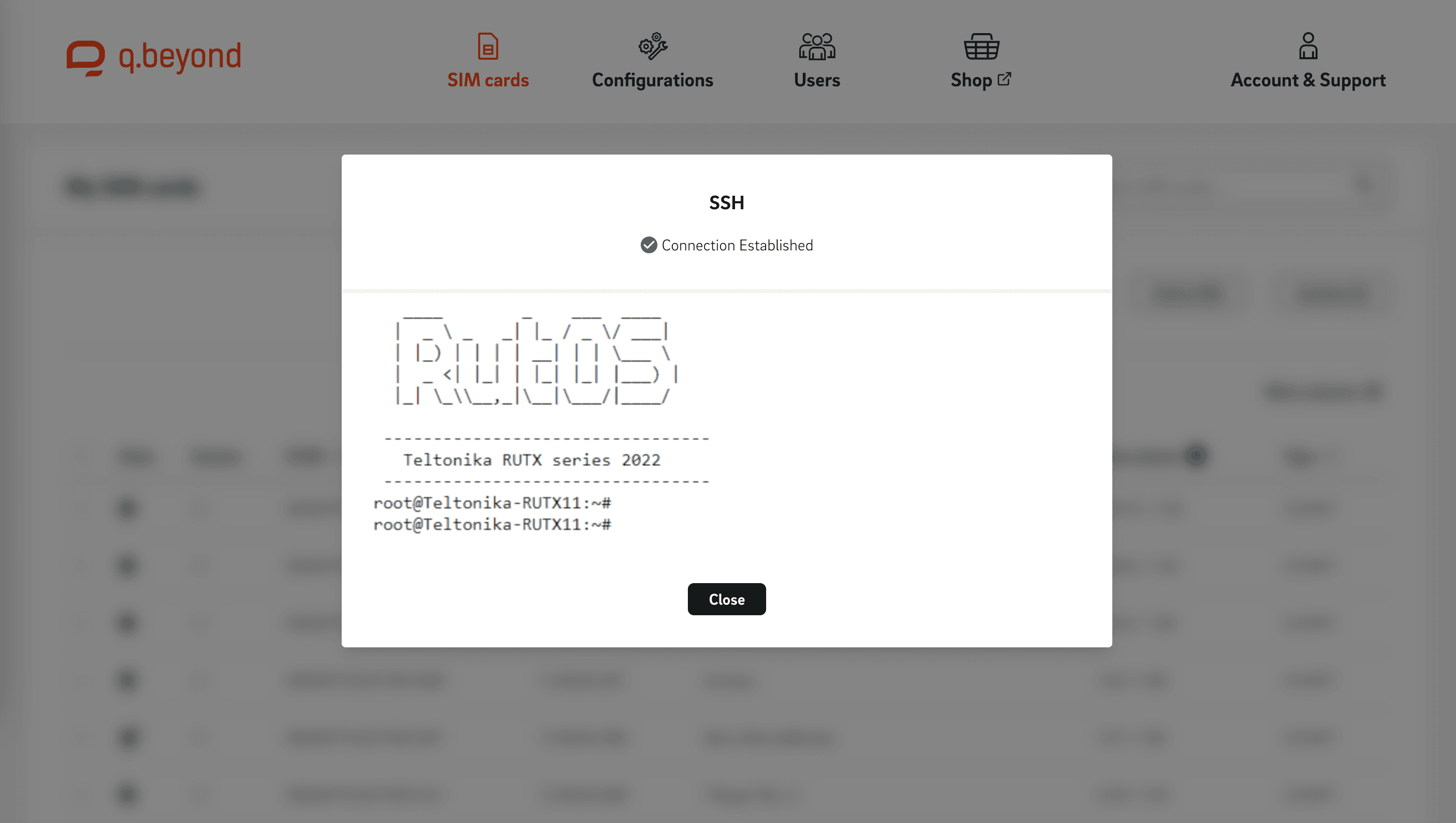
So, what is this SSH thing, you might ask? Well, it stands for Secure Shell. It is a protocol, which is like a set of rules, that lets you connect to another computer securely over a network that might not be secure at all. Think of your home Wi-Fi or even public internet connections; they are not always the safest places for sensitive information. SSH provides a secure channel, a bit like a private phone line, where no one can listen in on your conversation with the other computer. This connection can also be used for terminal access, which means you can type commands directly on the remote device, for file transfers, so you can send or receive documents, and for tunneling, which lets you send other kinds of network traffic through that secure line.
The `ssh` command, when you type it into your computer's terminal, tells your system to establish an encrypted, secure connection with a host machine. You usually tell it the `User_name` that represents the account you are trying to get into on that host. This tool is, in fact, a software package that makes secure system administration and file transfers possible over insecure networks. It is used in nearly every data center and in every large enterprise, so it is a pretty big deal in the world of computing. You know, it is very widely trusted.
Why SSH is a Must-Have for Your IoT Devices
Now, why would your little smart light bulb or your home weather station need something like SSH? Well, IoT devices are, by their very nature, connected to the internet, or at least to your home network. This connection makes them super convenient, but it also opens them up to potential dangers. Without a secure way to manage them, these devices could become easy targets for people with bad intentions. They might try to get into your network, steal information, or even use your devices for their own purposes, which is, you know, not good at all.
SSH helps with this a lot. It means you can manage remote servers via SSH, using both interactive SSH sessions, where you are typing commands in real time, and direct SSH commands, which can be part of automated scripts. This is super helpful for IoT because these devices are often left unattended and need to be accessed from afar. Maybe you want to update the software on your smart thermostat, or perhaps check the readings from a sensor in your garden. SSH gives you a safe way to do all of that. It provides that secure channel, keeping your data and your devices protected from unauthorized access, which is, honestly, a huge relief for anyone with smart gadgets.
The Principles Behind SSH: How It Keeps Things Safe
The secure shell (SSH) protocol sets up encrypted connections for remote logins and file transfers between computers. It is, in some respects, a very clever system that relies on a couple of key ideas to keep everything private and secure. Understanding these ideas can help you feel more confident about using SSH for your IoT projects. It is not just about typing a command; it is about knowing what is happening behind the scenes to protect your stuff.
Authentication: Making Sure It's Really You
One of the first things SSH does is make sure that the person trying to connect is actually who they say they are. This is called authentication. There are two main ways SSH handles this, offering different levels of checking. The simplest way is with a password. When you try to connect, the remote device asks for your password, and if it matches, you are in. However, passwords can be guessed or stolen, so there is a more secure method: SSH keys. These are like a very special, super-long digital key and lock set. You keep the private key on your computer, and the public key goes on the IoT device. When you try to connect, the two keys talk to each other to confirm your identity without ever sending your password over the network. This makes things much, much safer, truly.
Data Encryption: Keeping Your Information Private
Once you are authenticated, SSH starts encrypting all the data that passes between your computer and the IoT device. This means it scrambles the information in such a way that if someone were to intercept it, they would just see a jumble of meaningless characters. Only your computer and the IoT device have the special codes to unscramble it. This is why SSH is so good for sending sensitive commands or files; everything is kept private. It is like sending a secret message in a code that only you and your friend know. This is, you know, a very important part of its security.
Getting SSH Ready on Your IoT Device
Before you can connect to your IoT device, you will need to make sure it is set up to accept SSH connections. This usually means installing and enabling the SSH server software on the device itself. For many IoT devices, especially those running a version of Linux, this is a fairly straightforward process. For example, if you are working with a Raspberry Pi, it often comes with SSH already available, or it is very simple to get it going. You know, it is usually just a few steps.
Setting Up on Linux-Based IoT Devices
For many common IoT platforms, like a Raspberry Pi or other small computers running a Linux distribution, getting SSH ready is pretty simple. You might need to open a terminal on the device itself (if it has a screen) or connect a keyboard and monitor. Then, you would typically install the OpenSSH server package. A command like `sudo apt update` followed by `sudo apt install openssh-server` often does the trick on Debian-based systems. After that, you usually need to make sure the SSH service is running and set to start automatically when the device powers on. This makes it, you know, always ready for you.
Initial Connection From Your Computer
Once your IoT device has SSH ready, you can try to connect from your main computer. You will need the IP address or hostname of your IoT device. The basic command is `ssh user_name@your_iot_device_ip`. For instance, if your Raspberry Pi's username is `pi` and its IP address is `192.168.1.100`, you would type `ssh pi@192.168.1.100`. The first time you connect, your computer might ask you to confirm the remote device's identity. This is a security check to make sure you are connecting to the right place and not, you know, some imposter. You will then be prompted for the password for the `user_name` on the IoT device.
Connecting to Your IoT Gadget From Different Systems
Connecting to your IoT device using SSH looks a little different depending on what kind of computer you are using. Whether you are on a Linux machine, a macOS computer, or a Windows PC, there are good ways to get that secure connection going. This is, you know, pretty handy because everyone uses different setups.
From a Linux or macOS Computer
If you are using a Linux computer or a Mac, you are in luck! SSH is usually built right into the system, so you do not need to install anything extra. You just open your terminal application, which is a program where you type commands. To connect, you use the `ssh` command, just like we talked about earlier. For example, `ssh your_iot_username@your_iot_device_ip_address`. This command instructs the system to establish an encrypted secure connection with the host machine. It is quite straightforward, honestly, and works really well.
To effectively manage remote servers via ssh, use both interactive ssh sessions and direct ssh commands. This table provides an overview of frequently used commands:
- `ssh user@host`: Connects to a remote host.
- `ssh -p 2222 user@host`: Connects to a remote host on a specific port.
- `scp source_file user@host:destination_path`: Copies files securely.
- `sftp user@host`: Starts a secure file transfer session.
You can also discover key options for enhancing security and efficiency by looking into the `ssh` command's manual page, which you can usually access by typing `man ssh` in your terminal. It is, you know, a really powerful tool.
From a Windows Computer Using OpenSSH
For Windows users, things have gotten much easier recently. Modern versions of Windows often come with OpenSSH client software already installed, or you can add it through Windows features. This means you can use the `ssh` command directly in PowerShell or the Command Prompt, just like on Linux or Mac. In this tutorial, learn how to set up an ssh connection in Windows Terminal. You would open PowerShell, for instance, and type `ssh your_iot_username@your_iot_device_ip_address`. It is, you know, a very convenient way to connect.
You can also configure the `.ssh/config` file under Windows for more advanced setups. For example, you might want to set the host name and port in a config file for Windows, using OpenSSH through PowerShell. You would edit or create the file now by typing `notepad $HOME\.ssh\config` in PowerShell. Inside this file, you could put something like:
Host myiotdevice Hostname 192.168.1.100 Port 22 User myusername Then, you could simply type `ssh myiotdevice` to connect. This is, you know, a pretty neat way to simplify your connections, especially if you have many devices.
Using PuTTY for Windows Connections
For those Windows users who prefer a graphical tool, PuTTY is an SSH and Telnet client, developed originally by Simon Tatham for the Windows platform. PuTTY is open source software that is available with source code and is developed actively. It provides a straightforward window where you can enter the IP address or hostname of your IoT device, the port number (usually 22 for SSH), and then click "Open" to start the connection. It is a very popular choice for many, you know, because it is so easy to use.
Making SSH Even Smarter for IoT
Once you are comfortable with basic SSH connections, there are several ways to make your remote management of IoT devices even more efficient and secure. These methods help you save time and keep your setup well-organized. It is, you know, about getting the most out of SSH.
Going Password-Free with SSH Keys
Typing your password every time you connect can get old, and it is also less secure than using SSH keys. With SSH keys, you can achieve免密码登录, which means passwordless login, greatly improving remote operation efficiency. You generate a pair of keys: a private key that stays on your computer and a public key that you put on your IoT device. When you try to connect, the SSH client uses your private key to prove your identity to the server, which checks it against the public key. This process is automatic and very secure. It is, you know, a fantastic way to streamline access.
To set this up, you usually generate the keys on your computer using a command like `ssh-keygen`. Then, you copy the public key to your IoT device using `ssh-copy-id` or by manually adding it to the `~/.ssh/authorized_keys` file on the device. This is, you know, a one-time setup that pays off big time.
Organizing Your Connections with an SSH Config File
If you have multiple IoT devices, remembering all their IP addresses, usernames, and specific settings can become a bit of a headache. This is where the SSH config file comes in handy. It is a text file, usually located at `~/.ssh/config` on Linux/macOS or `%USERPROFILE%\.ssh\config` on Windows. In this file, you can create shortcuts and define specific settings for each device. For example, you can set a custom hostname and port. You know, it is like having a little address book for your SSH connections.
Let's say you want to use multiple SSH keys, so your key will get the name `id_rsa_test`. How do you configure the `.ssh/config` file under Windows so that it works with a usual Git server, or any other server? You could add entries like this:
Host myiotdevice1 Hostname 192.168.1.101 User iotuser IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_test Host myotherdevice Hostname another.iot.device.com Port 2222 User admin Then, to connect to `myiotdevice1`, you just type `ssh myiotdevice1`. This makes managing your connections much cleaner and simpler, truly. It is a very powerful feature for keeping things tidy.
Running Commands on Many Devices at Once
Sometimes, you might have multiple remote Linux machines, and you need to write a shell script which will execute the same set of commands in each machine. SSH makes this possible. You can include SSH commands directly within a script, allowing you to automate tasks across many IoT devices. For instance, a script could iterate through a list of IP addresses, connect to each one via SSH, and then run a command to update the software or collect data. This is, you know, incredibly useful for large-scale IoT deployments.
A simple example might look like this in a shell script:
#!/bin/bash DEVICES="192.168.1.100 192.168.1.101 192.168.1.102" for device in $DEVICES; do echo "Connecting to $device..." ssh iotuser@$device "sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y" echo "Update complete on $device." done This kind of automation saves a lot of time and makes sure that all your devices are, you know, consistently managed.
Transferring Files Securely
SSH is not just for terminal access; it is also great for moving files around securely. The `scp` (secure copy) command lets you copy files between your computer and your IoT device, or even between two remote devices, all over an encrypted SSH connection. For example, `scp my_data.txt iotuser@192.168.1.100:/home/iotuser/` would copy `my_data.txt` to the IoT device. There is also `sftp` (SSH File Transfer Protocol), which gives you an interactive file transfer session, much like FTP but with all the SSH security built in. You know, it is a very safe way to move your important data.
It is worth noting that while `sftp` is powerful, some users might look for a way to connect to an SFTP server using Windows File Explorer. The explorer has an option to connect to an FTP server but not a SFTP server directly. For SFTP, you would typically use a dedicated client like WinSCP or the `sftp` command line tool itself. This is, you know, just how it works.
Advanced Uses: X11 Forwarding and More
SSH can do even more. For instance, X11 forwarding allows you to run graphical applications from your IoT device and have their windows display on your local computer. If you run `ssh` and display is not set, it means SSH is not forwarding the X11 connection. To confirm that SSH is forwarding X11, check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in the verbose output of your SSH connection (`ssh -X -v`). This is, you know, pretty cool if your IoT device has graphical software you need to interact with.
SSH also allows for port forwarding, which can create secure tunnels for other network services. For example, you could forward a local port to a port on your IoT device, letting you access a web interface on the device as if it were running on your own computer, even if the device is behind a firewall. This is, you know, a very versatile feature.
Common Questions About SSH and IoT
People often have questions when they start using SSH with their IoT devices. Here are a few common ones that might come up:
How can I find my IoT device's IP address to connect with SSH?
You can usually find your IoT device's IP address by logging into your home router's administration page. It often lists all connected devices and their assigned IP addresses. Sometimes, the device itself might have a way to display its IP on a screen, or you can use network scanning tools on your computer. It is, you know, often just a quick look.
Is SSH truly secure enough for my smart home?
Yes, SSH is considered very secure when used correctly. It uses strong encryption and authentication methods. The main thing is to use strong passwords (if you are using passwords) or, even better, SSH keys. Make sure your private keys are kept secret and secure on your computer. Also, keep your IoT device's software updated to patch any potential vulnerabilities. It is, you know, all about good practices.
What if I cannot connect to my IoT device using SSH?
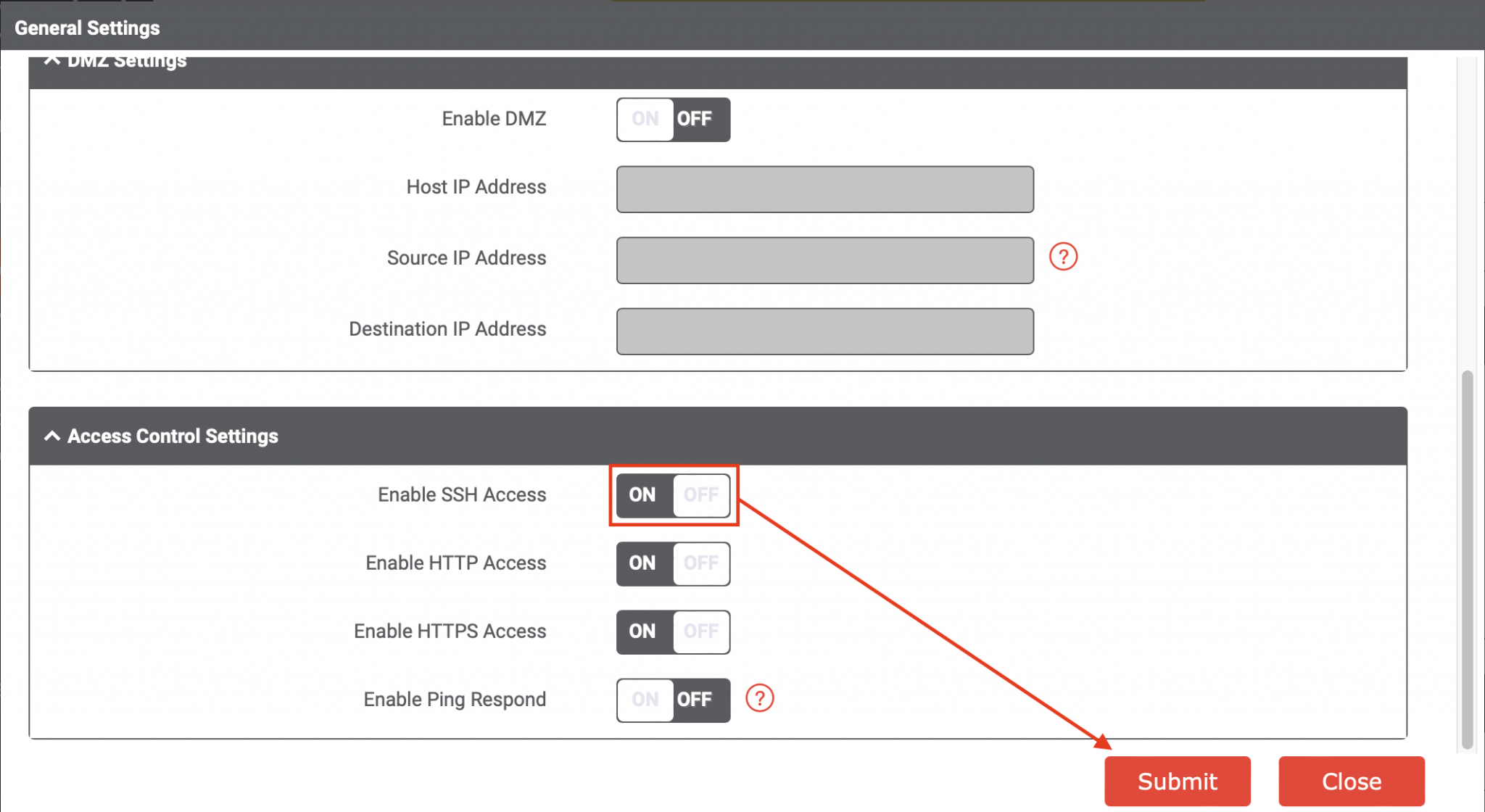
There are a few things to check. First, make sure the IoT device is powered on and connected to the network. Double-check the IP address or hostname you are using. Make sure the SSH server is actually running on the IoT device. Also, firewalls on either your computer or the IoT device might be blocking the connection; you might need to adjust their settings to allow traffic on port 22 (the standard SSH port). You know, sometimes it is just a small setting.
Keeping Your IoT Connections Safe for the Future
As we have seen, SSH provides a really strong foundation for securely managing your Internet of Things devices. It is, you know, an incredibly valuable tool for anyone who wants to keep their connected gadgets private and under their control. By understanding how SSH works, setting it up correctly on your devices, and using its more advanced features like passwordless logins and config files, you are taking a big step

Detail Author:
- Name : Gerhard Gerlach Sr.
- Username : dagmar54
- Email : bauch.esteban@kuphal.com
- Birthdate : 1990-01-12
- Address : 4473 Pollich Points North Price, NM 57605
- Phone : +1-325-550-8197
- Company : Cartwright-Hegmann
- Job : Architecture Teacher
- Bio : Veniam minus debitis sed tempora. Vel in voluptates impedit tempore. Facilis numquam et in quod. Perferendis laudantium est distinctio voluptatum.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/schaeferk
- username : schaeferk
- bio : Nihil ab alias id quibusdam ut qui. Omnis ut omnis non eius error.
- followers : 5920
- following : 776
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@kenny9350
- username : kenny9350
- bio : Aut in non sint est aspernatur.
- followers : 4914
- following : 682

