Ever wished you could check on your smart devices or tiny computers, like a Raspberry Pi, from anywhere in the world? It feels like magic, doesn't it? Well, it's actually quite doable, and this guide will show you how to set up remote IoT VNC behind your router, making your devices accessible and controllable no matter where you are. This kind of setup is pretty valuable for keeping tabs on things, especially if you have devices running in a different spot.
Controlling your IoT devices remotely, especially when they are tucked away behind your home or office router, is a truly helpful skill. It means you can manage smart sensors, automation systems, or even just check on a project without being physically there. This method, using VNC, gives you a visual way to interact with your device, just as if you were sitting right in front of it, which is rather convenient.
We'll walk through the whole process, from getting your device ready to making sure your connection is secure. We'll talk about how VNC and SSH tunneling work together, and even how some clever tools can make the process simpler. So, if you're ready to gain full control over your IoT gadgets from afar, you've come to the right place. It's actually a pretty straightforward path to remote access.
Table of Contents
- Why Remote IoT Access Matters
- Getting Your IoT Device Ready
- Understanding Router Challenges
- The VNC Connection: A Visual Bridge
- Secure Remote Access with SSH Tunneling
- Configuring Your Router for Remote Access
- Connecting to Your IoT Device from Anywhere
- Common Hurdles and Simple Solutions
- Bringing It All Together
Why Remote IoT Access Matters
Imagine you have a smart home setup, or maybe a small weather station powered by a Raspberry Pi in your backyard. What happens if you're away and need to tweak a setting or just see what's going on? That's where remote access comes in. It lets you interact with your devices as if you were right there, giving you a good amount of control.
The ability to access your IoT devices from a distance is becoming more and more important. With smart homes, businesses, and automation systems growing in popularity, having a reliable way to connect is pretty much essential. This kind of setup allows users to control and monitor IoT devices located within private networks, which is incredibly helpful.
This whole idea of remote IoT access behind a router is a really important part of today's network setups. It allows for smooth connections and control of smart devices. You can manage things, check data, or even fix small issues without needing to be physically present, which, you know, saves a lot of time and effort.
Getting Your IoT Device Ready
Before you can connect to your IoT device remotely using VNC, you need to make sure it's all set up and running properly. This initial preparation is, honestly, a very important step. It lays the groundwork for everything else we'll do.
Basic Setup for Your Device
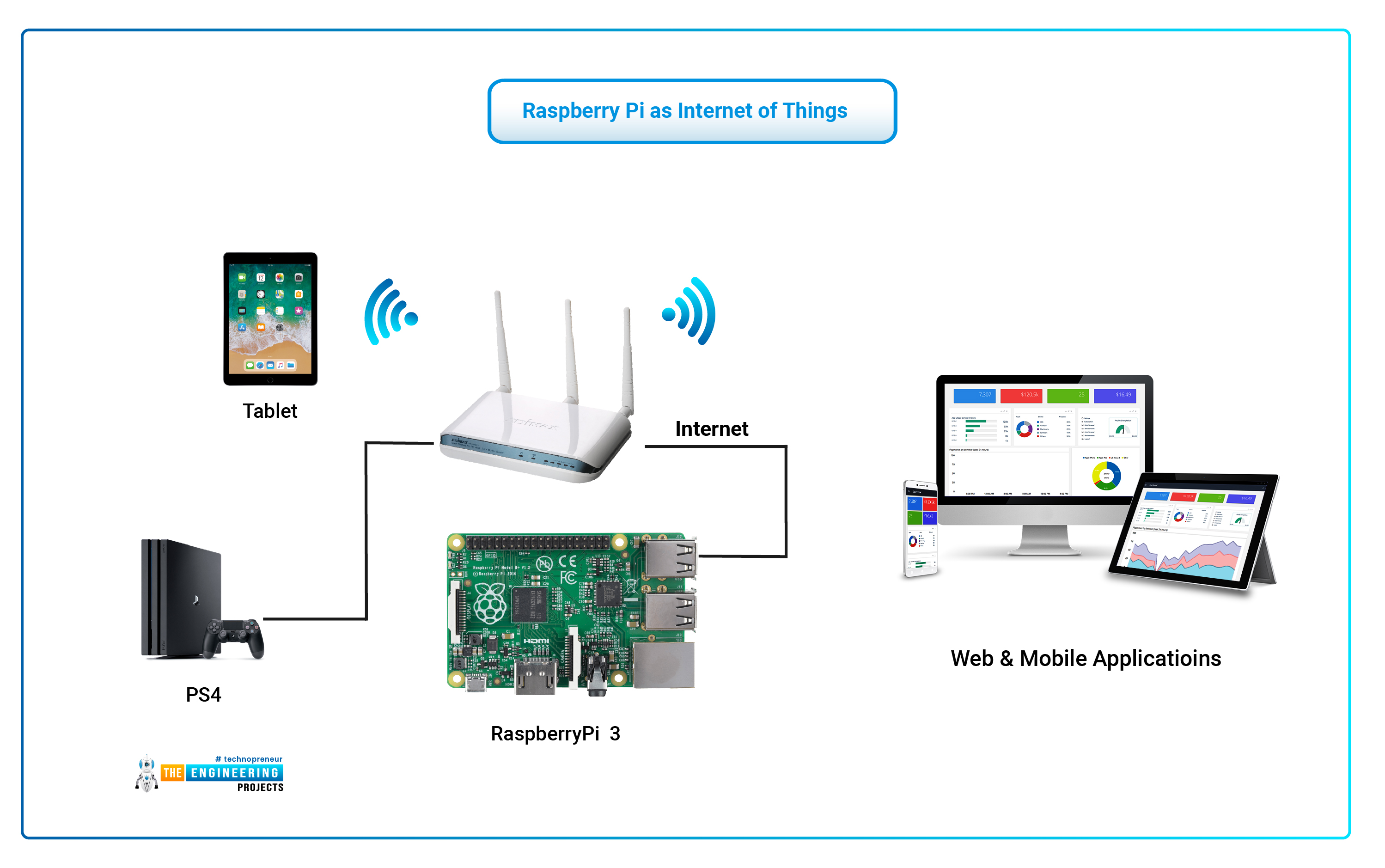
First things first, your IoT device needs to be alive and well. This means installing an operating system, like Raspbian if you're using a Raspberry Pi. You'll also want to connect your IoT device to a display, keyboard, and mouse for this initial setup, just to make things easier. This gets you ready for the next steps, you see.
For example, if you're using a Raspberry Pi, you'll burn the operating system image onto an SD card, then put that card into the Pi. After that, connect a monitor, keyboard, and mouse. Power it on, and you're ready to go through the basic configuration, which usually involves setting up a user and password, and maybe some language settings. It's a pretty standard procedure, really.
Internet Connection Essentials
Your IoT device also needs to be connected to the internet. An Ethernet cable often provides the most stable connection, but Wi-Fi works too, of course. A solid internet link is absolutely necessary for remote access, otherwise, how would you reach it? So, make sure your device can get online, as a matter of fact.
Check your device's network settings to confirm it has an IP address and can access websites. You might open a web browser on the device itself and try visiting a site, just to be sure. A reliable connection means fewer headaches later on when you're trying to connect from far away, which is pretty much the goal here.
Understanding Router Challenges
Routers are wonderful things, but they also create a bit of a barrier when you want to access devices inside your home network from the outside. They act like gatekeepers, protecting your internal devices from the wider internet. This is good for security, but it does add a step or two to our remote access plan, obviously.
What is a NAT Router?
Most home routers use something called Network Address Translation, or NAT. What this means is that your router has one public IP address for the whole internet, but all your devices inside your home have private IP addresses. When you send data out, the router translates your private IP to its public one, and when data comes in, it doesn't automatically know which internal device it's for. This is where the challenge comes in, you know.
Because of NAT, if someone from the internet tries to connect directly to your IoT device's private IP address, the router just won't know where to send that request. It's like trying to mail a letter to an apartment number without knowing the building's street address. So, we need a way to tell the router exactly where to send those incoming requests, which is what we'll get to.
Firewalls and Your Devices
Beyond NAT, your router also has a firewall. A firewall is like a security guard that checks all incoming and outgoing network traffic. It typically blocks unwanted connections from the internet to keep your network safe. This is a very good thing for security, but it means we need to make an exception for our VNC connection.
If your IoT device is behind a firewall or a router, you will likely need to configure something called port forwarding. This tells the firewall to allow specific types of incoming connections to reach your IoT device. Without this, your remote VNC connection would simply be blocked by the firewall, which, you know, defeats the purpose.
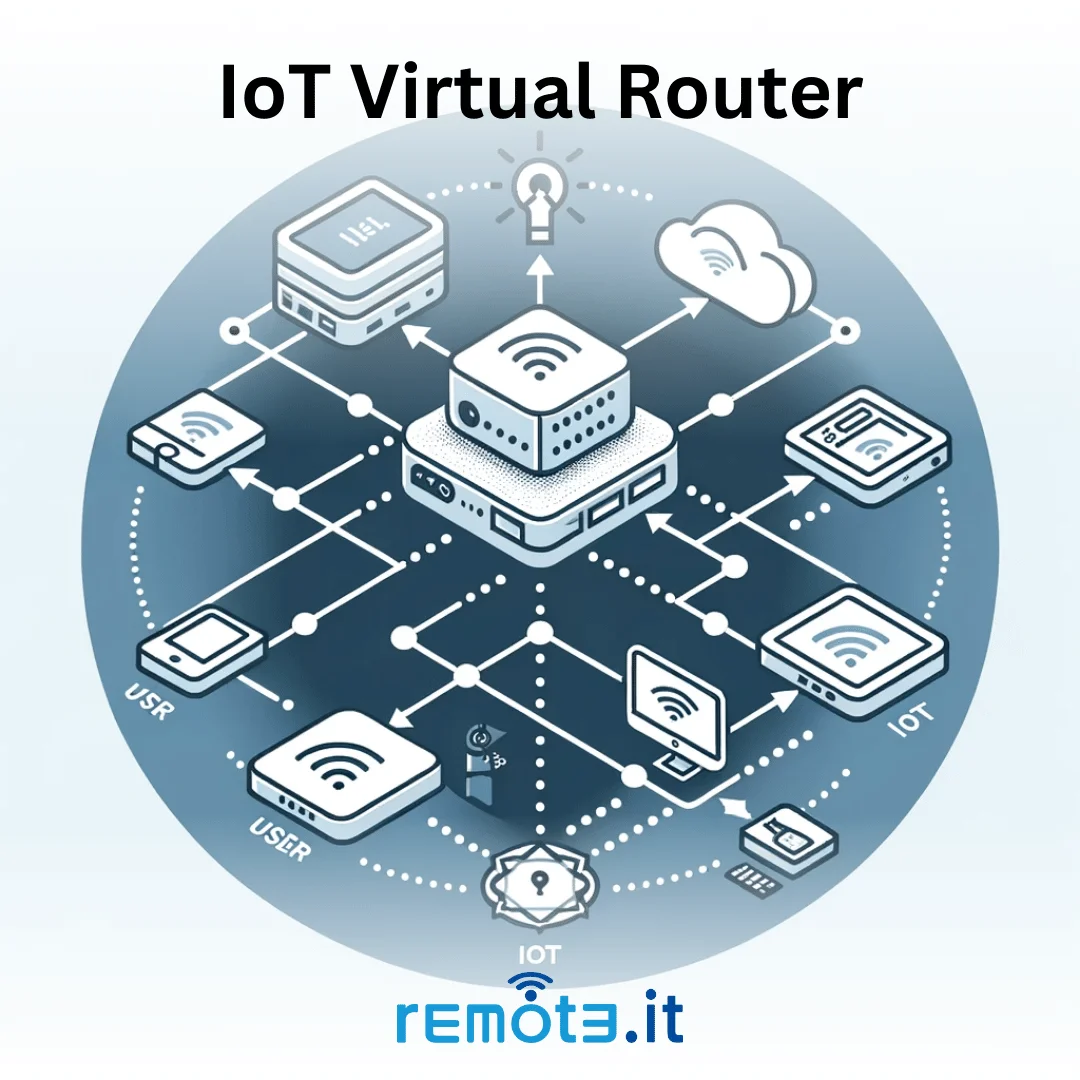
The VNC Connection: A Visual Bridge
VNC, or Virtual Network Computing, is the technology that lets you see and control your IoT device's desktop from another computer. It's like having a window into your device, letting you click, type, and interact just as if you were physically there. This remote control has become quite popular, you see, because it bridges the gap between physical and digital interactions.
What VNC Does for You
VNC allows you to remotely access, control, and manage your IoT device. This is especially useful for things like a Raspberry Pi, where you might not always have a monitor and keyboard attached. You get a full graphical interface, which is pretty handy for visual tasks or just checking on things. It's like having a remote desktop for your little computer, actually.
With VNC, you can open applications, browse files, run commands, and do pretty much anything you could do if you were sitting right in front of the device. This makes it a great tool for hobbyists, remote workers, and anyone managing a small fleet of devices. It's a very direct way to interact with your system, you know.
Installing VNC Server on Your IoT Device
To use VNC, you need to install a VNC server program on your IoT device. For a Raspberry Pi running Raspbian, RealVNC Connect is a common and fairly easy choice. You can usually install it with a few simple commands in the terminal. This sets up the part that listens for incoming VNC connections, which is, like, the key piece.
Here are the general steps to install a VNC server, typically on a Raspberry Pi:
- Open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi.
- Update your package list:
sudo apt update - Install the VNC server:
sudo apt install realvnc-vnc-server(or similar, depending on your OS). - Enable the VNC server to start automatically:
sudo systemctl enable vncserver-x11-service - Start the VNC server:
sudo systemctl start vncserver-x11-service - Set a password for your VNC connection. This is very important for security.
Once installed, the VNC server will be running in the background, waiting for you to connect. You'll want to remember the password you set, of course, as you'll need it later to get in.
Secure Remote Access with SSH Tunneling
Connecting directly to your VNC server over the internet can be risky because VNC connections aren't always encrypted by default. This is where SSH tunneling comes in. It creates a secure, encrypted pathway through your router, making your VNC connection much safer. It's a really smart way to protect your data, you know.
Why SSH Tunneling is a Smart Idea
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a protocol that allows for secure remote access to a computer. When you use SSH tunneling with VNC, you're essentially wrapping your VNC traffic inside an encrypted SSH connection. This means that anyone trying to snoop on your connection will only see encrypted data, which is pretty much unreadable to them. It's a very strong security measure.
Remote SSH access is a powerful tool for managing IoT devices behind a router. It's especially useful for devices in remote locations. By following the steps to set up SSH, you can establish a very secure and reliable connection. This kind of setup enhances both security and efficiency, which is a big plus.
Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device
Most Linux-based IoT operating systems, like Raspbian, come with SSH pre-installed or are very easy to add. You'll typically enable SSH through a configuration tool or a simple command. This allows your device to accept incoming SSH connections, which is the first step in creating our secure tunnel. So, make sure SSH is active on your device.
For Raspberry Pi, you can enable SSH using the `raspi-config` tool:
- Open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi.
- Type
sudo raspi-configand press Enter. - Go to "Interface Options" or "Interfacing Options".
- Select "SSH" and choose "Yes" to enable it.
- Reboot your Raspberry Pi if prompted.
Once SSH is enabled, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi using an SSH client from another computer. This connection itself is secure, and we'll use it to carry our VNC traffic, which is a clever trick, really.
Using Tools for Easy SSH Tunnels (Like Pinggy or SocketXP)
While you can manually set up SSH tunnels, tools like Pinggy or SocketXP make the process much simpler, especially when your router uses NAT and you don't want to mess with port forwarding. These services create a secure tunnel from your IoT device to their servers, and then you connect to their server, which redirects you to your device. It's a pretty neat solution, actually.
Using VNC with Pinggy SSH tunneling, for instance, allows you to securely and efficiently access and control IoT devices from anywhere. This setup is particularly valuable for managing devices that are behind tricky firewalls. Similarly, SocketXP secure SSH tunnels allow you to remotely access, control, and manage your IoT device securely over the internet. These tools handle the complex networking bits for you, which is a huge help, you know.
To use such a service, you typically install a small client program on your IoT device. This client then establishes an outbound connection to the service's server, creating a tunnel. Since the connection is initiated from inside your network, it usually bypasses router firewalls without needing port forwarding. You then use a special address provided by the service to connect to your device's VNC server, which is quite convenient.
Configuring Your Router for Remote Access
If you choose not to use a tunneling service like Pinggy or SocketXP, you'll need to configure your router directly. This involves setting up port forwarding, which tells your router to send specific incoming internet traffic to your IoT device. Proper router configuration is, you know, the backbone of a good remote IoT system.
The Role of Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is like telling your router: "Hey, any data coming in on this specific 'door' (port number) should go directly to this specific device (your IoT device's internal IP address) on this other 'door' (the VNC port, typically 5900)." This allows external computers to initiate a connection to your VNC server. It's a necessary step if you want direct access, you see.
Keep in mind that if your IoT device is behind a firewall or a router, you may need to configure port forwarding to allow incoming VNC connections. This involves setting up your router's rules. Without it, your external connection attempts will just hit a wall at your router, which is not what we want, obviously.
Steps to Configure Port Forwarding
The exact steps for port forwarding vary quite a bit depending on your router's brand and model. However, the general process is usually the same:
- Find your router's IP address: This is usually something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. You can often find it by checking your computer's network settings.
- Log in to your router: Open a web browser and type your router's IP address into the address bar. You'll need the router's username and password, which are often on a sticker on the router itself, or in its manual.
- Locate the Port Forwarding section: This might be under "Advanced Settings," "NAT," "Firewall," or "Virtual Servers." It varies a lot, so you might have to look around a bit.
- Create a new port forwarding rule:
- Service Port/External Port: This is the port number you'll connect to from the internet. You can choose any unused port, but for VNC, 5900 is common. If you use SSH tunneling, you might forward port 22 (SSH default) instead, and then tunnel VNC through that.
- Internal IP Address: This is the static IP address of your IoT device on your local network. Make sure your IoT device has a static IP so it doesn't change.
- Internal Port: This is the port your VNC server is listening on, typically 5900. If you're tunneling SSH, this would be 22.
- Protocol: Choose TCP, or sometimes TCP/UDP if available.
- Save the rule: Apply the changes, and your router should now direct traffic on that external port to your IoT device.
Remember, it's a good idea to assign a static IP address to your IoT device within your local network. This way, its IP won't change, and your port forwarding rule will always point to the correct device, which is quite important for consistent access.
Connecting to Your IoT Device from Anywhere
Once your IoT device is ready, VNC server is running, and your network is configured (either with port forwarding or a tunneling service), you're ready to connect. This is the moment you've been waiting for, you know, the part where it all comes together.
Using a VNC Client
To connect to your IoT device, you'll need a VNC client on the computer or mobile device you're using for remote access. RealVNC Viewer is a popular choice, available for many operating systems. You simply open the client and enter the address of your IoT device. This address will vary depending on your setup.
If you used port forwarding, you'll enter your home network's public IP address followed by the port you forwarded (e.g., `your.public.ip.address:5900`). If you're using an SSH tunneling service like Pinggy or SocketXP, you'll use the special URL or address they provide. You'll then be prompted for your VNC password, which is a good security measure, actually.
Testing Your Connection
After you've entered the connection details and your password, the VNC client should display your IoT device's desktop. Try moving the mouse, opening a program, or typing something. If everything works, congratulations! You've successfully set up remote VNC access to your IoT device behind your router. It's a pretty satisfying feeling, you know.
If you encounter issues, double-check all your settings: the VNC server on your device, the SSH tunnel (if used), and your router's port forwarding rules. Sometimes a simple typo or a forgotten password can cause problems. A bit

Detail Author:
- Name : Wayne Rutherford
- Username : lia75
- Email : okeefe.evangeline@ruecker.com
- Birthdate : 1972-12-02
- Address : 638 O'Keefe Groves West Ernestina, MA 41512
- Phone : 1-830-985-9457
- Company : Kulas Inc
- Job : Supervisor Correctional Officer
- Bio : Sed vitae modi est odio. Saepe aut et vel cum omnis. Sed non nihil sunt. Dolorum id reiciendis soluta.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/jeff_wiegand
- username : jeff_wiegand
- bio : Aliquam aut sed hic magnam.
- followers : 460
- following : 2744
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@wiegand2003
- username : wiegand2003
- bio : Rerum quibusdam qui sed ipsam qui odio sunt.
- followers : 3739
- following : 1927

